In the ever-evolving digital landscape, staying informed about the latest updates on websites can be crucial for various reasons. Whether you’re a researcher, a digital marketer, or just someone keen on the most recent information, knowing how to tell when a website was last updated is an invaluable skill. This article will guide you through eight effective methods to discover this information.
How To Find Out When A Website Was Last Updated
1. Check the Website’s Footer
When assessing the freshness of a website’s content, examining the footer can be a straightforward method. The footer typically contains important information about the site, including the date of the last update. This section is commonly found at the bottom of web pages and serves as a reference point for visitors seeking the most recent information. Let’s delve into the details of how to effectively check a website’s footer for the last update date.
Steps to Check the Website Footer
- Scroll to the Bottom: Navigate to the bottom of the webpage you are visiting. The footer is usually located here and is identifiable by its distinct positioning below the main content.
- Inspect Footer Content: Scan the footer for any text or information regarding the last update date. Look for phrases such as “Last Updated on,” “Page Modified on,” or similar indicators that specify when the content was last refreshed.
- Examine Date Format: Pay attention to the date format used in the footer. It may vary depending on the website’s design and geographic location. Common date formats include MM/DD/YYYY, DD/MM/YYYY, or written out in full (e.g., January 1, 2024).
- Note Time Zone: Keep in mind the time zone associated with the last update date, especially if the website caters to a global audience. This ensures accurate interpretation of the freshness of the content relative to your current location.
- Consider Frequency: Some websites update their content regularly, while others may have less frequent updates. Understanding the typical update frequency of the website can provide context when interpreting the last update date.
- Verify Accuracy: Confirm that the date provided in the footer corresponds to the content you are viewing. In some cases, websites may display the last update date for the entire site rather than specific pages.
Example of Website Footer
Below is an example of how the last update date might appear in a website footer:
| Copyright © 2024 Example Website. All rights reserved. |
| Last Updated on: January 15, 2024 |
In this example, the footer clearly states the date when the website’s content was last updated, providing visitors with valuable information about the currency of the information they are accessing.
2. Inspect the Source Code
For individuals with a deeper understanding of web technology, examining a website’s source code can provide valuable insight into its last update. By accessing the source code, users can locate specific metadata that includes details about when the webpage was last modified. This method requires basic familiarity with HTML and web development concepts. Let’s explore the steps involved in inspecting the source code of a website to uncover its last update information.
Steps to Inspect Website Source Code
- Access Source Code: Right-click on any part of the webpage and select “View Page Source” from the context menu. This action will open a new tab or window displaying the underlying HTML code of the webpage.
- Search for Metadata: Once the source code is displayed, use the search function (Ctrl + F) to locate relevant metadata containing details about the last modification of the webpage. Look for keywords such as “Last-Modified,” “Date,” or “Timestamp” within the HTML code.
- Analyze Timestamp Format: The timestamp format may vary depending on how the website is configured. It could appear as a Unix timestamp, a formatted date, or in a specific timezone. Understanding the format will help interpret the last update information accurately.
- Consider Cache Headers: Keep in mind that some websites may use cache headers to optimize performance by serving cached versions of pages. In such cases, the last update information in the source code may reflect when the page was last fetched from the server rather than when it was originally modified.
- Verify Accuracy: Ensure that the timestamp found in the source code corresponds to the content displayed on the webpage. Cross-reference the date with other sources of update information, such as the website footer or official announcements, to validate its accuracy.
Example of Source Code Metadata
Below is an example of how last update information might appear in the source code of a webpage:
<meta name="Last-Modified" content="2024-01-20T08:00:00Z">In this example, the meta tag “Last-Modified” includes a timestamp indicating that the webpage was last modified on January 20, 2024, at 8:00 AM UTC.
3. Use Browser Developer Tools

Modern web browsers are equipped with powerful developer tools that allow users to delve into the intricacies of web page construction. These tools offer a convenient way to access detailed information about the files loaded by a webpage, including their last modified dates. By utilizing browser developer tools, users can uncover valuable insights into the freshness of a website’s content. Let’s explore the steps involved in using browser developer tools to find last modified dates.
Steps to Use Browser Developer Tools
- Access Developer Tools: Open the webpage you wish to inspect in your preferred web browser. Right-click anywhere on the page and select “Inspect” from the context menu, or simply press the F12 key. This action will open the browser’s developer tools panel.
- Navigate to Network Tab: Within the developer tools panel, locate and click on the “Network” tab. This tab displays detailed information about the network requests made by the webpage, including the files loaded and their associated metadata.
- Reload the Page: To ensure you capture the most recent network requests, reload the webpage by pressing the refresh button or using the keyboard shortcut (Ctrl + R or Command + R). This action will populate the network tab with the latest data.
- Look for Last Modified Dates: Scan through the list of network requests to identify the files loaded by the webpage. Look for columns or sections indicating the last modified dates of these files. Common labels include “Last Modified,” “Last-Modified,” or “Date.”
- Analyze Timestamps: Pay close attention to the timestamps associated with each file. These timestamps indicate when the respective files were last modified or updated. Depending on the browser and website configuration, timestamps may be displayed in various formats, such as Unix time or human-readable date formats.
- Interpret Results: Interpret the last modified dates in the context of the webpage’s content and functionality. Consider whether critical files, such as CSS stylesheets, JavaScript scripts, or multimedia resources, have been recently modified, as these can significantly impact the user experience.
Example of Browser Developer Tools Output
Below is an example of how last modified dates might appear in the network tab of browser developer tools
| Filename | Last Modified |
| styles.css | Jan 20, 2024 08:30 AM |
| script.js | Jan 19, 2024 03:45 PM |
| image.jpg | Jan 18, 2024 11:20 AM |
In this example, the network tab displays a list of files loaded by the webpage along with their respective last modified dates, providing valuable information about the freshness of the webpage’s resources.
4. Leverage Online Tools
In addition to manual methods, users can leverage online tools specifically designed to ascertain the last update dates of websites. These tools streamline the process, offering convenience and efficiency in gathering essential information about website freshness. Let’s explore how these online tools work and how they can be utilized effectively.
Using Online Tools
- Search for Reputable Tools: Begin by searching for reputable online tools designed for checking website modification dates. Websites such as “Webpage Modified Checker” or “Last Modified” are popular options that specialize in this functionality.
- Navigate to the Tool’s Website: Once you’ve identified a suitable tool, visit its website by entering the URL into your web browser’s address bar. Alternatively, search for the tool’s name using a search engine, and click on the official link provided.
- Enter Website URL: Most online tools require users to input the URL of the website they wish to analyze. Locate the designated input field on the tool’s website and enter the URL of the website you want to check.
- Initiate Analysis: After entering the website URL, initiate the analysis process by clicking on the appropriate button or link. The tool will then begin scanning the specified webpage to retrieve relevant information about its last update date.
- Review Results: Once the analysis is complete, the online tool will typically display the last update date of the website along with additional details, such as the time of the last modification. Review the results carefully to gather the necessary information.
- Verify Accuracy: While online tools can provide valuable insights, it’s essential to verify the accuracy of the information obtained. Cross-reference the last update date obtained from the tool with other sources, such as the website footer or manual inspection, to ensure consistency.
Example of Online Tool Output
Below is an example of how the output from an online tool might appear:
| Website URL | Last Update Date |
| example.com | January 25, 2024 |
In this example, the online tool has retrieved the last update date of the specified website, indicating that it was last modified on January 25, 2024.
5. Consult the Wayback Machine
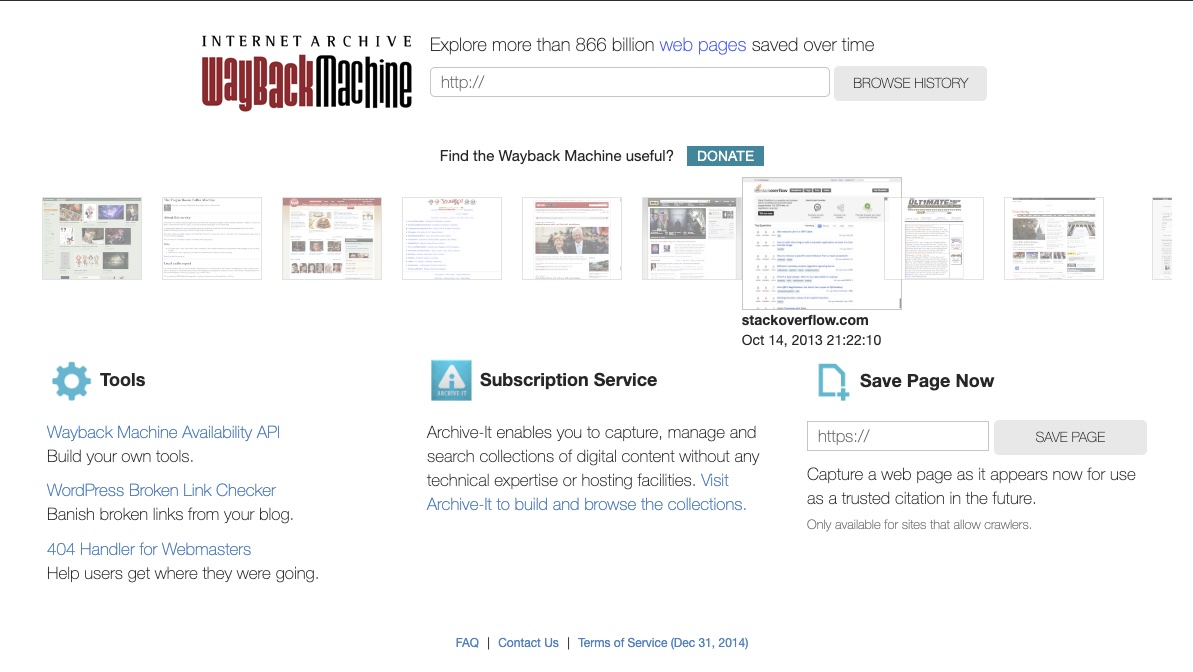
The Wayback Machine, hosted by archive.org, serves as a digital archive of the World Wide Web, allowing users to access historical versions of websites. This powerful tool enables individuals to explore the evolution of web pages over time, providing valuable insights into their update history and content changes. By consulting the Wayback Machine, users can uncover a wealth of information about a website’s past updates and revisions. Let’s delve into how to utilize this resource effectively for gaining a comprehensive understanding of website evolution.
Utilizing the Wayback Machine
- Access the Wayback Machine: Begin by navigating to the Wayback Machine website (archive.org) using your preferred web browser. The homepage features a search bar where users can input the URL of the website they wish to explore.
- Enter Website URL: In the provided search bar, enter the URL of the website you want to investigate. Ensure accuracy in typing the URL to retrieve relevant archival data. Click on the “Browse History” or similar button to proceed.
- Select Date Range: The Wayback Machine displays a calendar interface showing snapshots of the website taken on different dates. Users can select a specific date range to view archived versions of the website during that period. Alternatively, they can explore individual snapshots by clicking on specific dates highlighted in the calendar.
- Review Archived Versions: After selecting a date or date range, the Wayback Machine presents archived versions of the website corresponding to the chosen timeframe. Users can navigate through these versions to observe changes in content, layout, and functionality over time.
- Analyze Update History: Carefully examine each archived version of the website to discern patterns in updates and revisions. Pay attention to significant changes, such as design overhauls, content additions or removals, and alterations in functionality. Note any trends or intervals between updates to gain insights into the website’s update history.
- Retrieve Specific Information: Use the Wayback Machine’s features to extract specific information about past updates. Users can compare individual pages, view source code, and access additional metadata to deepen their understanding of website changes.
Example of Wayback Machine Interface
Below is an example of how the Wayback Machine interface might appear:
| Date | Archived Version |
| January 2022 | Snapshot 1 |
| March 2023 | Snapshot 2 |
| May 2024 | Snapshot 3 |
In this example, the Wayback Machine displays archived snapshots of a hypothetical website taken on different dates, allowing users to explore its evolution over time.
6. Check for Blog Posts or Articles
Blog posts and articles serve as valuable indicators of a website’s update frequency and content freshness. By examining the publication dates of these posts, users can gauge the website’s activity level and the recency of its information. This method provides a practical approach to evaluating the timeliness and relevance of the website’s content. Let’s explore how to effectively check for blog posts or articles to assess content freshness.
Steps to Check for Blog Posts or Articles
- Navigate to Blog or Articles Section: Start by visiting the blog or articles section of the website. Look for a dedicated tab or menu item labeled “Blog,” “Articles,” “News,” or similar. Alternatively, scan the homepage or navigation bar for links to recent posts.
- Scan Publication Dates: Once in the blog or articles section, scan the publication dates of the posts. These dates are typically displayed either at the beginning or end of each post. Look for recent dates to determine the freshness of the content.
- Look for Update Frequency: Pay attention to the frequency of blog posts or article publications. Websites that update their content regularly are likely to have a higher level of activity and provide more up-to-date information to their audience.
- Check for Date Sorting Options: Some websites offer sorting options that allow users to arrange blog posts or articles by publication date. Utilize these sorting features to easily identify the most recent content.
- Consider Content Relevance: In addition to publication dates, consider the relevance of the blog posts or articles to the website’s overall theme or niche. Fresh content should address current topics, trends, or developments in the respective industry or subject matter.
- Verify Consistency: Ensure that the publication dates of blog posts or articles align with other indicators of content freshness, such as the website footer, metadata, or manual inspection. Consistency across multiple sources enhances confidence in the accuracy of the assessment.
Example of Blog Post Dates
Below is an example of how publication dates might appear on a website’s blog posts:
- Blog Post Title 1
Published: January 10, 2024
- Blog Post Title 2
Published: February 5, 2024
- Blog Post Title 3
Published: March 20, 2024
In this example, the publication dates of three blog posts indicate recent activity on the website, suggesting ongoing content updates.
7. Look for Copyright Dates

Copyright dates, commonly located in a website’s footer section, can offer clues about the last update or modification. While copyright dates may not always directly reflect the most recent changes to a website’s content, they can still provide valuable context regarding the website’s overall maintenance and upkeep. Let’s delve into how copyright dates can be used to infer the last update, along with their limitations.
Analyzing Copyright Dates
- Footer Inspection: Begin by scrolling to the bottom of the webpage to locate the footer section. Copyright information is typically displayed here, along with other legal disclaimers and notices.
- Focus on Copyright Year: Direct your attention to the copyright year mentioned in the footer. This year indicates when the copyright was initially established or last updated.
- Consider Recent Year Changes: Note if the copyright year matches the current year or if it differs. If the copyright year matches the current year, it may suggest recent updates or maintenance of the website’s content.
- Review Website Activity: Take into account other indicators of website activity, such as blog posts, article publication dates, or the presence of new features or announcements. These factors can provide additional context regarding the frequency of updates and the relevance of the content.
- Verify Other Sources: While copyright dates can provide insights, they should be corroborated with other sources of update information, such as blog posts, metadata, or manual inspection. This helps ensure a comprehensive understanding of the website’s update history.
Limitations of Copyright Dates
- Static Copyright Year: Some websites may display a static copyright year that does not change annually. In such cases, the copyright date may not accurately reflect recent updates to the website’s content.
- Automated Updates: Websites may update their content without necessarily updating the copyright year. Automated systems or periodic content refreshes may not trigger changes to the copyright information.
- Manual Updates: Inconsistencies in updating copyright information manually can also lead to inaccuracies. Website owners or administrators may overlook updating the copyright year even after making significant content changes.
8. Use SEO Browser Extensions
SEO (Search Engine Optimization) browser extensions, such as MozBar or SimilarWeb, offer valuable insights into various aspects of a website, including its update frequency. These extensions provide users with data and metrics related to a website’s performance, traffic, and content updates. By leveraging SEO browser extensions, users can gain valuable information about how frequently a website’s content is updated, helping them assess its freshness and relevance. Let’s explore how to utilize these extensions effectively to determine update frequency.
Steps to Use SEO Browser Extensions
- Install the Extension: Begin by installing the desired SEO browser extension from the respective browser’s extension marketplace. Popular options include MozBar, SimilarWeb, and SEMrush.
- Activate the Extension: Once installed, activate the extension by clicking on its icon in the browser toolbar. This action opens the extension’s interface, where users can access various features and data points related to website analysis.
- Enter the Website URL: Input the URL of the website you wish to analyze into the extension’s search or input field. Some extensions may automatically detect and display data for the currently visited website.
- Navigate to Update Frequency Data: Explore the extension’s interface to locate information about the website’s update frequency or content freshness. This data may be presented in different sections or tabs, depending on the specific features offered by the extension.
- Review Update Metrics: Examine the metrics and indicators provided by the extension related to the website’s update frequency. Look for data points such as the frequency of content updates, the freshness of the content, or the last update date.
- Analyze Trends: Evaluate any trends or patterns in the update frequency data. Note whether the website demonstrates consistent updates over time or if there are periods of inactivity or stagnation.
- Consider Other Factors: While update frequency data from SEO browser extensions can be valuable, it’s essential to consider other factors such as the nature of the website, its industry, and the type of content being published. These factors can influence the expected update frequency and content freshness.
Example of Update Frequency Data
Below is an example of how update frequency data might be displayed in an SEO browser extension:
| Website | Update Frequency |
| example.com | Regular updates every week |
In this example, the SEO browser extension indicates that the website example.com receives regular updates every week, providing valuable insight into its update frequency.
Conclusion
Understanding how to tell when a website was last updated is a key digital literacy skill in today’s information age. By employing these eight methods, you can stay ahead in the digital information game, ensuring you’re always working with the most current data available.
FAQ
Yes, it can be reliable, but it requires some technical knowledge to interpret the data correctly.
Not always. Some websites may not update their copyright year regularly.
They provide a good estimate but may not always be 100% accurate.
Not necessarily. It’s one of many indicators and should be considered alongside others.
It can be a good indicator, but it’s not infallible. Some websites may not actively use social media.